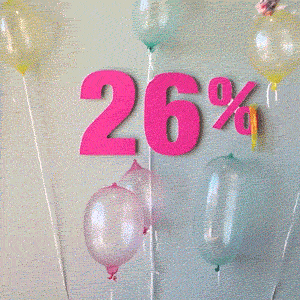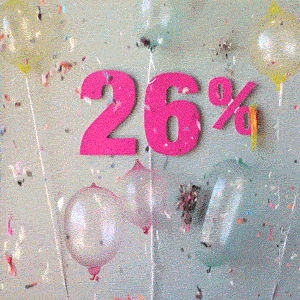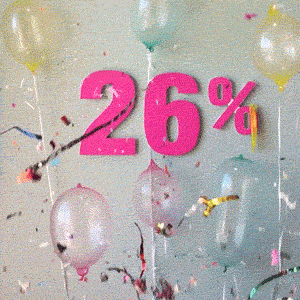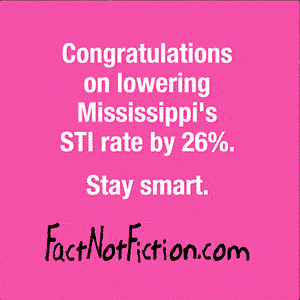What is it?
BV is an infection caused when too much of certain bacteria change the balance of bacteria in the vagina. It is the most common vaginal infection in women, ages 15-44.
BV is not considered an STI, but having BV can increase your chances of getting one. BV may also affect women who have never had sex.
How do I keep from getting it?
Having a new sex partner or multiple sex partners and douching can upset the balance of bacteria in the vagina and put women at increased risk for getting BV.
Although doctors do not understand how BV is spread, the following prevention steps may help lower your risk of developing BV:
- Not having sex
- Limiting your number of sex partners
- Not douching
How do I know if I have it?
Many women with BV have no symptoms. If you do have symptoms, you may notice a thin white or gray vaginal discharge, odor, pain, itching, or burning in the vagina. Some women have a strong odor, especially after sex. You may also have burning when urinating; itching around the outside of the vagina, or both.
Can it be cured or treated?
BV will sometimes go away without treatment. But if you have symptoms of BV you should be checked and treated. It is important that you take all of the medicine prescribed to you, even if your symptoms go away. A health care provider can treat BV with antibiotics, but BV can recur even after treatment.
Male sex partners of women diagnosed with BV generally do not need to be treated. However, BV may be transferred between female sex partners.
If you don’t get treated, BV can cause some serious health risks:
- Increasing your chance of getting HIV if you have sex with someone who is infected with HIV
- Making it more likely that you will deliver your baby too early if you have BV while pregnant
- Increasing your chance of getting other STIs, like chlamydia and gonorrhea
If you need to see a doc about BV, visit our website for help locating a Mississippi clinic near you: https://www.factnotfictionms.com/clinics